PHP设计模式笔记:使用PHP实现模板方法模式
【意图】
定义一个操作中的算法的骨架,而将一些步骤延迟到子类中。Template Method 使得子类可以在不改变一个算法的结构的情况下重定义该算法的某些特定的步骤【GOF95】
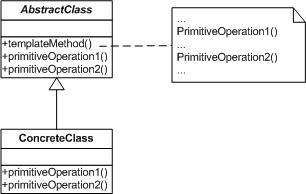
【模板方法模式结构图】
【模板方法模式中主要角色】
抽象模板(AbstractClass)角色: 定义一个或多个抽象方法让子类实现。这些抽象方法叫做基本操作,它们是顶级逻辑的组成部分。
定义一个模板方法。这个模板方法一般是一个具体方法,它给出顶级逻辑的骨架,而逻辑的组成步骤在对应的抽象操作中,这些操作将会推迟到子类中实现。同时,顶层逻辑也可以调用具体的实现方法
具体模板(ConcrteClass)角色:实现父类的一个或多个抽象方法,作为顶层逻辑的组成而存在。
每个抽象模板可以有多个具体模板与之对应,而每个具体模板有其自己对抽象方法(也就是顶层逻辑的组成部分)的实现,从而使得顶层逻辑的实现各不相同。
【模板方法模式适用场景】
1、一次性实现一个算法的不变的部分,并将可变的行为留给子类来实现。
2、各子类中公共的行为应被提取出来并集中到一个公共父类中以避免代码重复。
3、控制子类扩展。
【模板方法模式与其它模式】
1、策略模式(strategy模式):模板方法使用继承来改变算法的部分,策略模式使用委托来改变整个算法。区别在于封闭的变化不同,一个变化的部分,一个变化的是整体。
2、工厂方法模式(factory method模式):Factory Method模式常被模板方法调用。
【模板方法模式PHP示例】
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 | <?php /** * 模板方法模式简单示例 2010-09-12 sz * @author phppan.p#gmail.com http://www.phppan.com * 哥学社成员(http://www.blog-brother.com/) * @package design pattern */ /** * 抽象模板角色 * 定义抽象方法作为顶层逻辑的组成部分,由子类实现 * 定义模板方法作为顶层逻辑的架子,调用基本方法组装顶层逻辑 */ abstract class AbstractClass { /** * 模板方法 调用基本方法组装顶层逻辑 */ public function templateMethod() { echo 'templateMethod begin.<br />'; $this->primitiveOperation1(); $this->primitiveOperation2(); echo 'templateMethod end.<br />'; } /** * 基本方法1 */ abstract protected function primitiveOperation1(); /** * 基本方法2 */ abstract protected function primitiveOperation2(); } /** * 具体模板角色 * 实现父类的抽象方法 */ class ConcreteClass extends AbstractClass{ /** * 基本方法1 */ protected function primitiveOperation1() { echo 'primitiveOperation1<br />'; } /** * 基本方法2 */ protected function primitiveOperation2(){ echo 'primitiveOperation2<br />'; } } /** * 客户端 */ class Client { /** * Main program. */ public static function main() { $class = new ConcreteClass(); $class->templateMethod(); } } Client::main(); ?> |
【模板方法模式】
模板方法是一种代码复用的基本技术,模板方法导致一种反射的控制结构,这指的是一个父类调用子类的操作。
其实现过程:准备一个抽象类,将部分逻辑以具体方法以及具体构造子的形式实现,然后声明一些抽象方法来迫使子类实现剩余的逻辑。不同子类可以以不同的方式实现这些抽象方法,从而对剩余的逻辑有不同的实现。
【重构的原则】
重构时应当遵守的原则是:将行为以是移到结构的高端,而将状态尽量移动到结构的低端。
Auer曾在文献【AUER95】中指出:
1、应当要所行为而不是状态定义一个类。
2、在实现行为是,是用抽象状态而不是用具体状态。
3、给操作划分层次。
4、将状态的确认推迟到子类中。在父类中,如果需要状态属性的话,可以调用抽象的取值方法,而将抽象的取值方法的实现放到具体子类中。
如果可以遵守以上的而,那么就可以在等级结构中将接口与实现分离,将抽象与具体分离,从而保证代码可以最大限度的被复用。